
by Nicholas Mitsakos | China, commodities, Economy, Investments, The Market, Writing and Podcasts
Beyond 2022, higher interest rates and slower global growth most likely trigger a market correction, perhaps at an exorbitant cost. As discounts rates rise and growth assumptions lower, many stocks based assumptions that low interest rates and high growth would sustain for many years will see dramatic repricing and much lower valuations.
Energy and commodities, and the businesses associated with them, are in for a very bumpy ride, but there is a fundamental sustainability to their cash flow and long-term attractiveness as world supply reorders. That which is essential prevails.
The luxury of thinking we have halcyon days of global growth and geopolitical stability may not be with us for some time to come. It is perhaps time to plan for that now.

by Nicholas Mitsakos | Book Chapter, Investment Principles, Investments, Writing and Podcasts
Investment models that account for uncertainty, volatility, and failure succeed in the long term. Events in Ukraine, oil and natural gas markets, commodities, supply chain disruption, and spiking inflation highlight that, while none of these were predictable, all represent increasing uncertainty permeating all markets. The pandemic and war in Ukraine were unforeseen, but that’s just the point, unforeseen events will occur. It is a waste of time to try to predict the specifics, it is an essential investment strategy to manage risk to not only withstand but profit from “certain uncertainty.” Irrationality, not only in human behavior (with unfortunate, often tragic results) but market movements, investment volatility, and bewildering prices, is another certainty. “Mr. Market” as Benjamin Graham said, “is an irrational schizophrenic.” Investing as if he is not assures an investment strategy that will ultimately fail. An increasing number of growth and momentum investment funds are shutting down after sustaining significant losses recently, a sign of the severe pain the selloff in growth stocks is inflicting. More importantly, it signals an inability for investment funds to manage risk and understand that markets and investments do not move in a singular direction for long, and the correction is sudden and painful – regardless of how compelling “momentum” may seem. Risk management is the key to investment sustainability, but this seems to go ignored among most investment professionals. Frequent and extreme volatility is here to stay, and that is likely to decimate growth and momentum funds, as well as highly leveraged equity investment funds (from LTCM in 1998 to Archegos in 2021, the lesson is never learned for long – and there will be more examples to come). Clear and coherent markets, free from political agenda, bad compromises, and ineffective regulation are almost nonexistent. The consequences continue to be pyrotechnic.

by Nicholas Mitsakos | China, Economy, Investment Principles, Investments, Public Policy, Writing and Podcasts
Collectively, the world is good at screaming about all sorts of immediate and looming crises, whether that is climate change, totalitarian governments abusing civilians and trampling on personal rights or outright genocide. A speech and a prayer suffice but we’re not going to do anything. Donation websites, lighting buildings in flag colors of abused nations, and sending hopes and prayers accomplish nothing. We send prayers. We just won’t answer them. The Ukraine war’s consequences are severalfold. Economically, global consequences may be slower and less spectacular than the dramatic Russian military invasion. But, the effects will permeate the global economy, and Russia will be the biggest long-term loser. While this does not comfort families suffering and dying in the streets of Ukrainian cities, it realigns global industries and economies, strengthens the West, and is likely to galvanize United States’ leadership in the global economy – setting up even more intense rivalry China. A big uncompromising response now is the most likely strategy to settle these dramatic issues – and if it leads to regime change in Russia, that helps everyone, especially the Russians. The US and the EU need to grow up and start acting like global leaders.

by Nicholas Mitsakos | Book Chapter, Investments, Technology, The Market, Transformative businesses, Writing and Podcasts
Transformation, Valuation, Employment, and Deflation
Disruption to some of the world’s most important industries, deflationary pressure caused by scaling lower-cost businesses, and sustained low interest rates challenge traditional valuation models. Technological platforms, from blockchain-based businesses to energy storage to DNA sequencing, enable unprecedented disruption to business and economic models.
Interest rates will remain low, equity values will remain high, innovation will drive deflationary pressure, and volatility will be intense and frequent. A new approach is required to understand dynamic global competition and sustainable value.
by Nicholas Mitsakos | Economy, Investment Principles, Investments, The Market, Writing and Podcasts
Investors expected that the Fed would not only end its bond buying program, but many believed it would also raise interest rates. While the Fed did agree to taper its bond buying, essentially decreasing its $150 billion monthly bond buying program by $15 billion per month, ending the program in 2022. However, the Fed kept interest rates the same and clearly signaled that it would not raise interest rates anytime soon, and almost definitely not until the taper of its bond buying was completed – in other words, not for at least one more year.
Investors who had been betting on the Fed raising interest rates wagered on the yield curve flattening for Treasuries. Therefore, they invested in short-term Treasuries believing those would outperform longer-term Treasuries, as well as 10-year and 30-year bonds. Instead, we are seeing the opposite happen. Short-term bonds are dropping in price and yields are approaching their highest levels since March 2020. Meanwhile, prices for long-term bonds have climbed. This same phenomenon is happening for government bonds that only in the United States, but also in the UK, Canada, and elsewhere.

by Nicholas Mitsakos | Economy, Investments, The Market, Writing and Podcasts
There are warning signs that the stock market is transitioning from some form of reality to misguided euphoria. The S&P 500 is up almost 10% in the last 30 days. However, this broad optimism doesn’t seem to be matched by many forms of fundamental reality.
Earnings are barely moving, and profit margins are under pressure from higher wages and rising product costs. However transitory one imagines supply chain constraints and lack of available workers, the situation has certainly extended much further than most predicted.

by Nicholas Mitsakos | Book Chapter, Currency, Digital Assets, Investments, Technology, Writing and Podcasts
Decentralized finance (DeFi) can disrupt global finance – but only if Defi systems and central governments cooperate. Yes, sworn enemies cooperating for the greater good.
While each seems to be the sworn enemy of the other, ultimately, a cooperative relationship between decentralized and efficient (versus anachronistic and cumbersome) financial infrastructure and government central banks with stable currencies is absolutely necessary.
Defi transactions, to scale globally, require stable and predictable value. Government-issued currencies are the only reliable and foreseeable foundation. Cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin were never currencies. They are a sideshow that will remain a speculative asset, and increasingly unimportant.
Cryptocurrencies represent an architectural shift in how financial infrastructure and technology interact, and therefore, it is disrupting how the financial industry works globally. It is neither a new kind of money system nor a danger to economic stability. It is more important than that.

by Nicholas Mitsakos | Biotechnology, Book Chapter, Health Care, Investments, Writing and Podcasts
Investors have been swept up in the notion of “philanthropic capitalism” and have targeted life-sciences as an avenue that can fulfill this benefit to society. While laudable in concept, this is non-scientific surrealism. “Hoped-for” is not a reliable business model, and most of the unrealistic goals would not be sustainable even if achieved. Real science and innovation are more impactful and substantial and make life sciences even more.
by Nicholas Mitsakos | Book Chapter, Investment Principles, Investments, Writing and Podcasts
Distinguishing what’s happening in the market and the direction of important market metrics – the signal – from garbled, inconsistent, and mostly useless data – the noise – is extremely challenging today. Information is contradictory and transient making data and critical events more confusing and indistinguishable. Unusual circumstances brought about by the pandemic, subsequent supply chain interruptions, inconsistent production and demand, and unclear economic forecasts combined for almost unprecedented uncertainty and unpredictability.
Typically, near-term predictions are reasonable and reliable because we have immediately available and fairly accurate data making short-term predictions reasonably accurate. In other words, we can estimate what will happen because we have a good idea what just happened. But this is not the case today. Predictions based on the near-term past are more muddled now than ever. While we used to be able to say we can see a trend, whether that’s inflation, economic growth, or some other important metric, too much volatility, irrelevance, and lack of applicability (after all, who is going to project from a base that includes a pandemic impacting global supply chains and production?), we really can’t reasonably rely on any of that data to try to find a trend or connect the dots generating a near-term forecast with any meaningful depth of data and understanding
More intense volatility occurring more often will be characteristic of this market from now on. An investment strategy must withstand and profit from this. The only clear signal from the market is that there is far too much noise and not enough of a clear signal. Without clarity, determining an investment strategy is flying blind with no instruments.
Core holdings combined with an ability to withstand and profit from volatility and unpredictability are essential for investors today.
by Nicholas Mitsakos | Book Chapter, Investment Principles, Investments, Writing and Podcasts
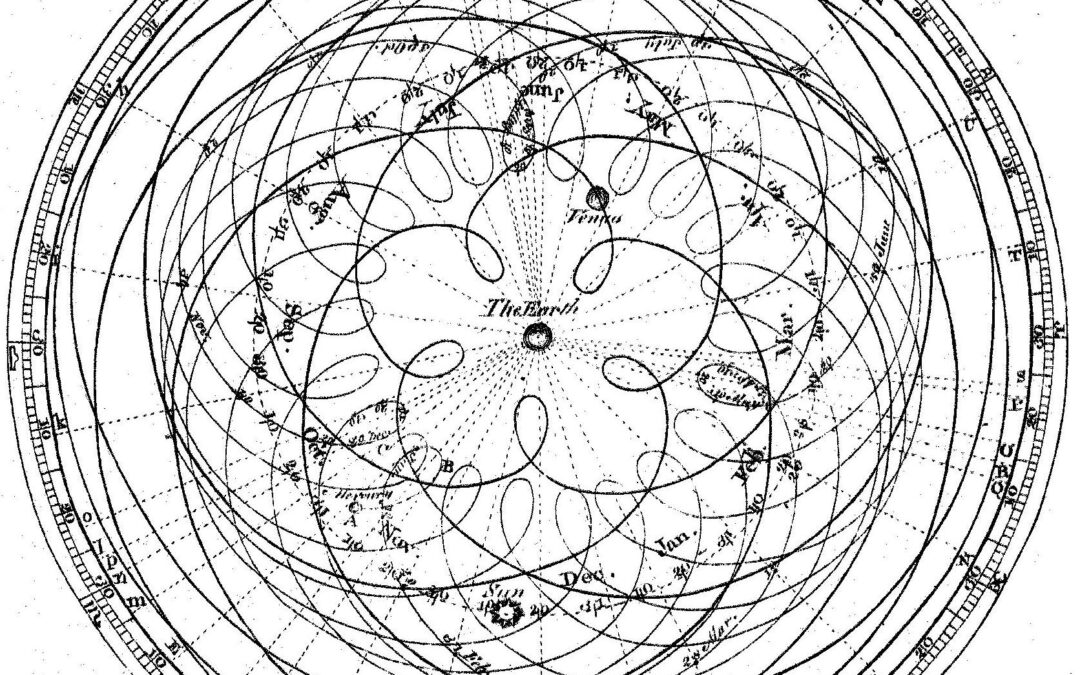
Assume nothing, new models and analytical tools, coupled with constant revision, questioning everything, reassessing, and re-analyzing, are essential to success in today’s markets. Often, and we are seeing that in today’s market, relying on bad assumptions, dogma, or prior belief can be disastrous.
This story about medieval astronomy applies directly to investment strategies, market valuations, and portfolio construction today. It’s the same lesson –begin by questioning the very assumptions on which an entire system is built. There is also a very specific application of this model that is particularly current.
One of the most valuable lessons is to assume no knowledge and analyze closely every initial assumption. Nothing is so obvious that it can’t be questioned. Unexamined ideas and assumptions will eventually be useless. Any assumptions and any model used to explain and predict anything (whether it’s the movement of planets or financial markets) needs to go back to first principles and discard any assumptions, preconceived knowledge, or bias.

by Nicholas Mitsakos | Artificial Intelligence, Book Chapter, Digital Assets, Finance, Investments, Public Policy, Technology, Writing and Podcasts
Technology is facing a substantial crossroads as policy changes with global resonance, such as China’s new crackdown on the country’s big tech companies (such as Ant Financial and Didi Global), the rising resistance to social media behemoths like Facebook, and the need for governments, whether in the United States, Western Europe, or China, to manage and control technological development. Regardless of any good intentions, this will add friction, inefficiency, and underperformance to the most dynamic global industry. The best intentions usually bring disastrous consequences. China cannot escape the law of unintended consequences. Trying to “manage” innovation and creativity takes away the often unplanned and serendipitous breakthroughs that make many significant advancements possible in the first place. From an economic perspective, capital is not going to invest in an uncertain environment where prosperity is managed and, despite great risk where most ventures will fail, the truly successful ones which make up for the losses and encourage capital to keep investing, will be mitigated. The vanguard of capital flight from China is beginning, and it will not ease if this policy and attitude are not revised. This attempt at “fairness and more equal distribution” will do nothing more than keep capital away and stifle any attempt at creativity, technical innovation, and economic advancement. The intention of this policy will yield the opposite outcome as a consequence. The signal means substance. Substance means innovation, creativity, and competitive dynamics that create the most effective innovations, the best solutions, and the most sustainable companies. Central planning, bureaucratic industrial policy, government-led economic management, and dictatorial focus have always failed, and always will. The US should not fall into this trap, regardless of how appealing it may be.
It is only noise.

by Nicholas Mitsakos | Book Chapter, Economy, Investments, Writing and Podcasts
Separating signal versus noise is challenging these days because today’s signal is more muddled than ever. One of the more unusual circumstances, which I covered in more detail in the article “Important and Unknowable” is that the immediate past is telling us extraordinarily little about the near future. That is unusual because we can typically estimate the near-term by connecting the dots with reasonable depth and data from the recent past.
One of the reasons why people have inflation fears, currency tremors, market jitters, and emotional vacillation between joy and terror is that all these outcomes seem equally likely that any sense to realistically gauge the directions of these key metrics. We can usually rely upon near-term data to predict the near-term future, and that usually gives us a reasonable sense of comfort about the markets, and how to plan, prepare, predict, and withstand anticipated market moves. But that does not seem to be the case now.












